Pterygium
Pterygium
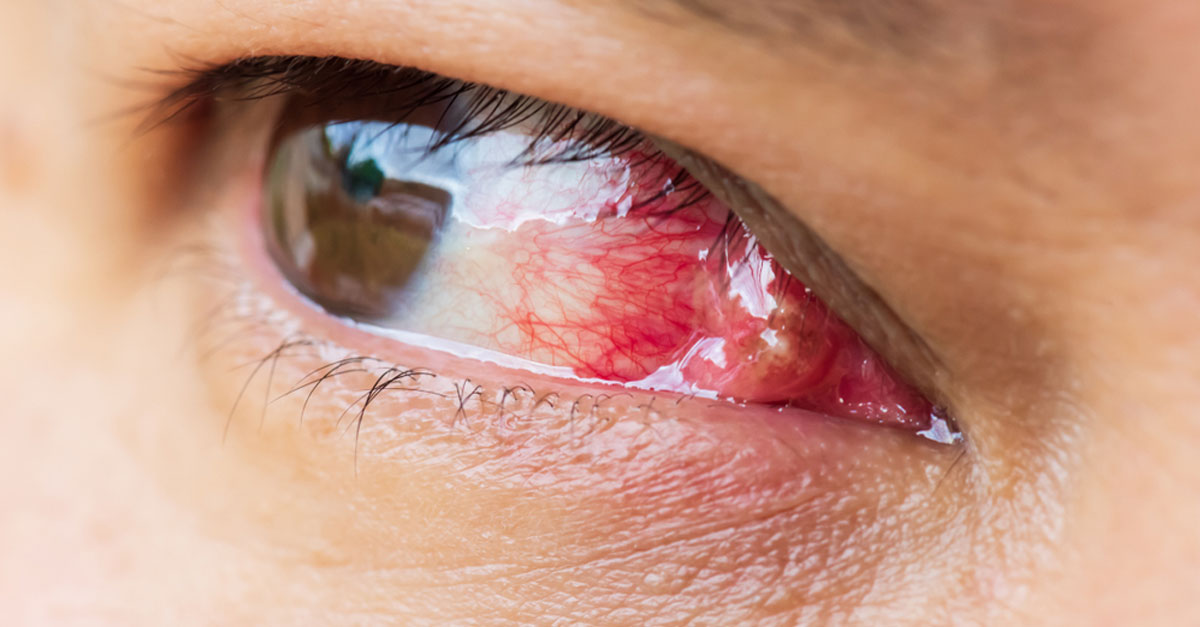
What is Pterygium?
Pterygium is a common non-cancerous growth that develops on the conjunctiva. The conjunctiva is the clear thin tissue that covers the white part of the eye.
Pterygium may develop in one or both eyes. It is characterized by a pinkish triangular-shaped mass that starts in the inner corner of the eye and extends towards the cornea.
What are the symptoms of Pterygium?
- Pinkish, triangular-shaped tissue growth of the conjunctiva
- Usually appears on the nasal side
- Color varies from pink to red
- Eye irritations like burning, redness, tearing or foreign body sensation
What causes Pterygium?
The exact cause of Pterygium is not known. It can be small or may grow large enough to interfere with vision.
- It usually occurs in people who spend most of their time outdoors, with frequent or excessive exposure to sunlight or wind.
- Exposure to UV light seems to have a role.
- Genetic predisposition
What are the treatment options?
Treatment usually depends on the size of the Pterygium.
- In very mild cases, when the pterygium is small, not increasing , and not causing any symptoms, no treatment is required, and can be only observed.
- Dr Sneha may prescribe eyedrops, or glasses to help with symptoms
- If the pterygium is large or vision is affected or if you are very symptomatic, then Dr. Sneha may recommend surgery to remove it. There are many different ways of doing the surgery, and Dr Sneha will discuss and suggest the best option for you.
What does surgery entail?
It is performed as a day care procedure, with discharge on the same day. It is usually performed under local anesthesia and may take 20min to an hour. An eye patch may be placed over the eye at the end of the procedure.The most common technique used today involves a simple excision of the pterygium combined with conjunctivo-limbal Auto grafting.
During the procedure, the pterygium is removed and the gap in the conjunctiva, left by the removal of the pterygium, is filled with conjunctival graft taken from the upper outer quadrant from the same or opposite eye. The graft is held in place either with sutures or glue. The stem cells present in the limbal area is known to help prevent recurrences
Laser treatment is given when there is a larger growth towards the center of the cornea. An excimer laser is used to smooth the surface irregularities and improve the vision.
What is the recovery time?
The recovery time is usually short. You can get back to normal routine within a week after the surgery.
What are the potential complications?
- Scarring and perforation of the cornea
- Blurred vision
- Soreness or irritation in the eye
- Redness of the eye
- Pterygium is infamous for reccurence, although newer technologies and techniques have dramatically reduced its frequency. It may reccur in the 1st 12 months following surgery.
